Using the Mailgun REST Destination Component
The REST Destination Component is an SSIS data flow pipeline component that can be used to write data to Mailgun REST services.
See Mailgun Rest Connection Manager for how to connect to Mailgun and see Mailgun REST Source Component for how to retrieve data from Mailgun.
There are three pages for configuration:
- General
- Columns
- Error Handling
General Page
The General page allows you to specify general settings for the REST Destination component.

- Connection Manager
-
The destination component requires a REST connection to Mailgun. The Connection Manager drop-down will show a list of all connection managers that are available for your current SSIS package.
- Destination Object
-
The Destination Object option allows you to specify which object to write data to. A drop-down with the available objects is listed here.
- Action
-
The Action option allows you to specify how data should be written to Mailgun.
Note: Supported actions may vary from object to object depending on Mailgun's API document.
- Input Time Zone
-
The Input Time Zone option specifies the timezone of all incoming datetime fields. Available options are:
- UTC
- Local
- Refresh Component Button
-
Clicking the Refresh Component button causes the component to retrieve the latest metadata and update each field to its most recent metadata.
- Map Unmapped Fields Button
-
By clicking this button, the component will try to map any unmapped attributes by matching their names with the input columns from upstream components.
- Clear All Mappings Button
-
By clicking this button, the component will reset (clear) all your mappings in the destination component.
- Expression fx Icon
-
Click the blue fx icon to launch SSIS Expression Editor to enable dynamic updates of the property at run time.
- Generate Documentation Icon
-
Click the Generate Documentation icon to generate a Word document that describes the component's metadata, including relevant mapping, and so on.
Columns Page
The Columns page of the REST Destination Component allows you to map the columns from upstream components to the REST Fields. On this page, you can select the object whose columns you wish to configure in the top-left drop-down.

On the top left of the grid, you can see a checkbox, which can be used to toggle the selection of all available fields. This is a productive way to check or uncheck all available fields.
On the Columns page, there is a grid that contains four columns as shown below.
- Input Column: You can select an input column from an upstream component for the corresponding REST Field.
- REST Field: The field that you are writing data to.
- Data Type: This column indicates the type of value for the current field.
- Unmap: This column can be used to unmap the field from the upstream input column, or otherwise, it can be used to map the field to an upstream input column by matching its name if the field is not currently mapped.
- Manage Custom Fields
-
This button is only available when working with the Messages destination object. This button will open the manage custom fields dialog in order to add any custom fields to write to the Message object.

In the dialog page, you would see a grid that contains two columns:
- Column: You can add the name of the custom field you want to write to.
- Data Type: This column indicates the type of value for the selected field.
Error Handling Page
The Error Handling page allows you to specify how errors should be handled when they happen.

There are three options available:
- Fail on error
- Redirect rows to error output
- Ignore error
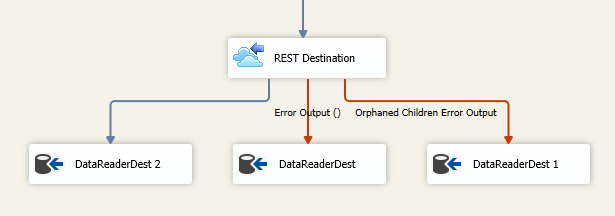
When the Redirect rows to error output option is selected, rows that failed to write to the target REST service will be redirected to the 'Error Output({PrimaryInputName})' output of the Destination Component; rows from the Child Input that failed to find the parent records will be redirected to the 'Orphaned Children Error Output' output of the Destination Component. As indicated in the screenshot below, the blue output connection represents rows that were successfully written, and the red 'Error Output{PrimaryInputName}' and 'Orphaned Children Error Output' connection represent erroneous rows.
- Error Output({PrimaryInputName})
- ErrorCode: Contains the error code that is reported by the target service or the component itself
- ErrorColumn: Contains the name of the column that is causing the error. Note that this column is not always populated
- ErrorMessage: Contains the error message that is reported by the target service or the component itself
- Orphaned Children Error Output
- ErrorCode: Contains the error code that is reported by the target service or the component itself from the Child Inputs
- ErrorColumn: Contains the name of the column that is causing the error from the Child Inputs. Note that this column is not always populated
- Input Name: Contains the name of the Child Input that is having an issue.
- Column Name: Contains the name of the column that is having an issue in the specific Child Input.
- Column Value: Contains the value of the column that is having an issue in the specific Child Input.
- Parent Input Name: Contains the Parent Input name of the specific Child Input.
- Parent Column Name: Contains the name of the column that is having an issue in the specific Parent Input.
On the Error Handling page, there is also an option that can be used to enable or disable the following output field for the destination component.
- _MailgunId: Contains the newly created Mailgun record's ID, which you can use to write to log or further process using additional data flow components.
- _ResponseBody: Contains the body of the response received from the endpoint in raw format.
Note: If you don’t plan to use this field for any further processing, it is generally recommended to turn them off, so you don’t get any warning from SSIS about fields that are not used. It should also provide slightly better performance by doing so.

